Cardiovascular disease (CVD) affects the heart and blood vessels. It is essential to know about CVD, one of the leading causes of illness worldwide. This article will simplify the key aspects of CVD, helping patients recognize symptoms, understand causes, and learn about prevention and treatment options.
What Is Cardiovascular Disease?
Cardiovascular Disease refers to a group of diseases that involve the heart and blood vessels. It includes conditions like heart attacks, strokes, coronary artery disease, and heart failure. These diseases can interfere with the heart’s ability to pump blood or the blood vessels’ ability to circulate blood effectively. The result may be life-threatening complications if left untreated.
How Common Is Cardiovascular Disease?
Cardiovascular disease has a widespread impact on millions of people across the globe. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports it as the top killer worldwide, taking almost 18 million lives every year. It causes about 30% of all deaths in many countries. While older adults face higher risks, lifestyle choices put younger people at growing risk too. In wealthy nations, poor diets, lack of exercise, and high obesity rates often lead to the disease.
In contrast, poor countries see more cases due to limited healthcare access and increased smoking. Worryingly, younger people now show more instances of the disease because they eat more processed foods and move less. Health campaigns around the world aim to tackle this growing problem.
Programs that push for better eating habits, regular workouts, and quitting smoking play a key role in lowering disease rates. Yet, we need more team efforts to address the root causes and make prevention easy for everyone.
What are the Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease?
The symptoms of the disease can differ based on the specific condition. Common signs to be aware of include:
Chest Pain or Discomfort
It is one of the most common symptoms many heart patients experience. You may feel pressure or squeezing in the chest, and it often radiates to the arms. In addition, the pain may come on suddenly or get worse with physical activity or emotional stress. If the discomfort lasts for more than a few minutes, then you should immediately seek medical attention.
Shortness of Breath
It is a common symptom of heart failure, where you may feel unable to pump blood effectively. You can experience shortness of breath during physical exertion such as walking and climbing. If you witness such symptoms, then seek medical attention.
Fatigue
If you experience consistent fatigue that is not relieved by rest, then it can be a sign of cardiovascular disease. It occurs when the heart is not pumping blood effectively. It leads to less oxygen and nutrients reaching the muscles and tissues.
Dizziness or Fainting
It occurs when there is reduced blood flow to the brain, which is a possible sign of a heart condition. It may cause blockage in the heart. You may experience dizziness or fainting, along with chest pain.
Palpitations
You experience palpitation when there is an irregular heartbeat or a sensation of racing. It also occurs due to stress, anxiety, or physical activity. This symptom is also seen with chest pain and dizziness.
Swelling In The Legs, Ankles or Feet
If you notice swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet, then it might be a sign of fluid retention. It occurs when the heart is not able to pump effectively. The excess fluid builds up in the legs and ankles. It causes a noticeable puffiness.
Pain In Other Areas
Pain during a heart attack is not always limited to the chest. In addition, it can radiate to other parts of the body, including the arms, neck, jaw, or back. You may witness a dull ache, pressure, or tightness. This pain occurs with other symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, or shortness of breath.
What Conditions are Cardiovascular Diseases?
Cardiovascular diseases include a variety of conditions, such as
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
It occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries. It restricts the blood flow to the heart, which leads to chest pain. In addition, it increases the risk of heart attacks. Over time, it can weaken the heart’s ability to function properly.
Heart Attack
You may witness a heart attack when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked. It is usually a blood clot. Without proper blood supply, the affected area of the heart muscle begins to die. It is recommended to take timely treatment.
Stroke
You may experience a stroke when there is a disruption in the blood flow to the brain. It also occurs due to the rupture in the blood vessels. A minor stroke can lead to permanent brain damage.
Heart Failure
When the heart is not able to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, you may experience heart failure. It also causes conditions like CAD, high blood pressure, or prior heart attacks.
Arrhythmias
It refers to abnormal heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation. In this condition, the heart beats irregularly and sometimes too quickly or too slowly. In addition, this condition can cause dizziness and shortness of breath.
Hypertension
It is a common condition many people experience in their 30s or 40s. It can damage the heart and blood vessels over time. It can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
Peripheral Artery Disease
It occurs due to the narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the limb. It may result in poor circulation, causing symptoms such as leg pain, cramping, and weakness.
The major cause of the disease is fatty deposits in the blood vessels, a condition known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this buildup narrows the arteries, limiting blood flow. The list of diseases is never-ending, but it is important to understand each condition. Understanding the types of the disease will help you be informed and prevent future health challenges.
What are the Risk Factors?
It is a major health crisis that is affecting millions of people. Hence, it is essential to recognise the risk factors for better health management. The risk factors are usually generalised into modifiable and non-modifiable groups.
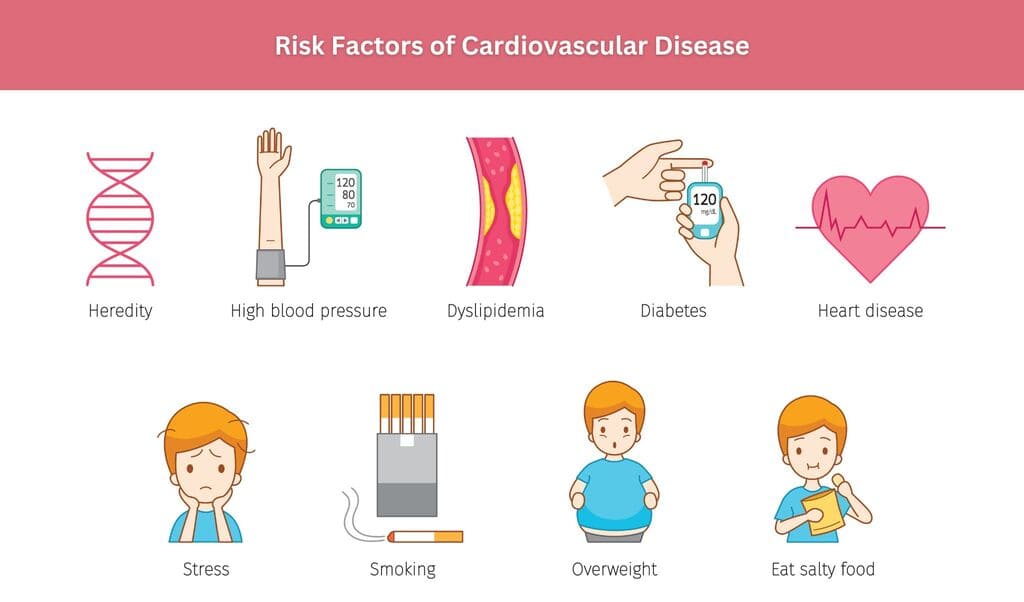
Non-modifiable Risk Factors
These risk factors that we cannot change include:
- Age: The symptoms of CVD rise with age, which is around the age of 45.
- Gender: Men usually have a higher risk, and women usually face the risk after menopause.
- Family History: If you have any background in heart disease or stroke in the family, it can increase an individual’s risk.
- Ethnicity: There are different groups, such as South Asians and African Americans, that are more prone to CVD.
Modifiable Risk Factors
These are factors related to lifestyle and health that can be altered:
- High Blood Pressure: Known as hypertension, this condition makes the heart work harder, raising the chances of heart attacks and strokes.
- High Cholesterol Levels: High levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and low levels of HDL (good cholesterol) can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Smoking: The use of tobacco damages blood vessels and speeds up plaque accumulation.
- Poor Diet: A poor diet that is high in saturated fats, trans fats, salt, and sugar can lead to obesity and elevated cholesterol levels.
- Physical Inactivity: Physical inactivity contributes to a sedentary lifestyle, which raises the risk of obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.
- Obesity: Obesity itself puts extra strain on the heart and heightens the chances of developing hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- High Blood Sugar: Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels.
- Chronic Stress: Chronic stress may result in unhealthy coping strategies, such as overeating or smoking.
By tackling modifiable risk factors through lifestyle adjustments, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine medical checkups, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of heart and blood vessel disease. Prevention is key to maintaining a healthy heart. After understanding the meaning of cardiovascular disease, let’s understand how to diagnose the disease.
How Can a Heart Condition Be Identified?
CVD is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests that assess the health of the heart and blood vessels. Early detection is vital for effective disease management.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors begin by examining the patient’s medical history, looking for symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations. They also evaluate risk factors such as age, family history, smoking habits, and lifestyle choices. During the physical exam, they check blood pressure, heart rate, and signs of fluid retention, such as swollen legs.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are conducted to measure cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), which indicate inflammation. Blood sugar tests can help identify diabetes, a condition that increases the risk of CVD.
Tests Might You Have for the Disease
To confirm a diagnosis, doctors may suggest specific tests, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Echocardiogram: Sound waves are used to create images of the heart.
- Stress Tests: These assess how the heart functions under physical exertion.
- Blood Tests: These check cholesterol levels and markers indicating heart damage.
- Angiography: X-rays are used to visualize the blood vessels.
- CT or MRI Scans: These provide detailed images of the heart and its vessels.
When Is the Right Time to See Your Doctor?
You should consult a healthcare provider if you notice any chest pain, shortness of breath, unexplained fatigue, swelling in the limbs, or any similar symptoms in the family history.
Regular check-ups are also crucial for monitoring your heart health and identifying any potential problems early on. Make sure to visit the doctors to find the symptoms and understand the cardiovascular disease treatment. There are various heart and blood vessel disease examples, and understand that there is a treatment for every health concern.
What Can Be Expected Following Cardiovascular Disease Treatment?
If you wish to recover from the disease, it can be a transformative journey. It offers a second chance to lead a better life. Here’s what you can do and expect after the treatment:
Lifestyle Changes
The doctor will try to elaborate about health-lifestyle habits. The doctors will recommend some diet changes, such as reducing salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats. It also incorporates more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. In addition, the doctor will suggest regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga. It encourages strengthening the heart and enhances overall health.
Medications
The doctor will prescribe medicines that help to manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels or prevent blood clots. It is important to take these as directed and maintain regular follow-ups to monitor their effectiveness.
Emotional Well-being
You may experience mixed emotions, including relief, anxiety, or even depression. Hence, you can join support groups, seek counselling, or practice stress management techniques.
Routine Check-up
The doctor will suggest routine check-ups, such as blood tests and heart imaging. These help track progress and detect potential health issues. Feel free to talk with your health expert, who can help address any health concerns.
After understanding cardiovascular disease definition, it is important to comprehend the symptoms, pre-treatment, and post-treatment. The cardiovascular disease symptoms are not difficult to predict in the first attempt.
Conclusion
If you have any concerns or risk factors, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider for early diagnosis and tailored care. A healthy heart is essential for a healthy life, and it’s never too late to prioritize your heart health. You can also request an appointment to visit our cardiology and vascular care center for more information on treatment and conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Are the Key Indicators That Suggest a Patient May Be at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease?
Ans: The key indicators include high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, physical activity, and a poor diet. In addition, age and gender also influence risk, with men usually at higher risk at an earlier age. Besides, patients with symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness should also be evaluated promptly.
Q2. When Should a Patient With Cardiovascular Disease Be Referred to a Cardiologist?
Ans: If the patient experiences unexplained chest pain and witnesses abnormal results from diagnostic tests. In addition, if a patient’s condition worsens despite the initial treatment or if there are other complications such as heart failure or severe valvular disease. In all these scenarios, the patient should be consulted for further evaluation and management.
Q3. How Does a Heart Expert Monitor a Patient’s Progress After a Heart Attack?
Ans: The doctor will recommend regular follow-up visits, blood tests, and imaging to assess the heart function and recovery. Besides, the key metrics include blood pressure, cholesterol levels, ECGs, and echocardiograms. It helps to evaluate heart function and detect any complications like arrhythmias or heart failure.