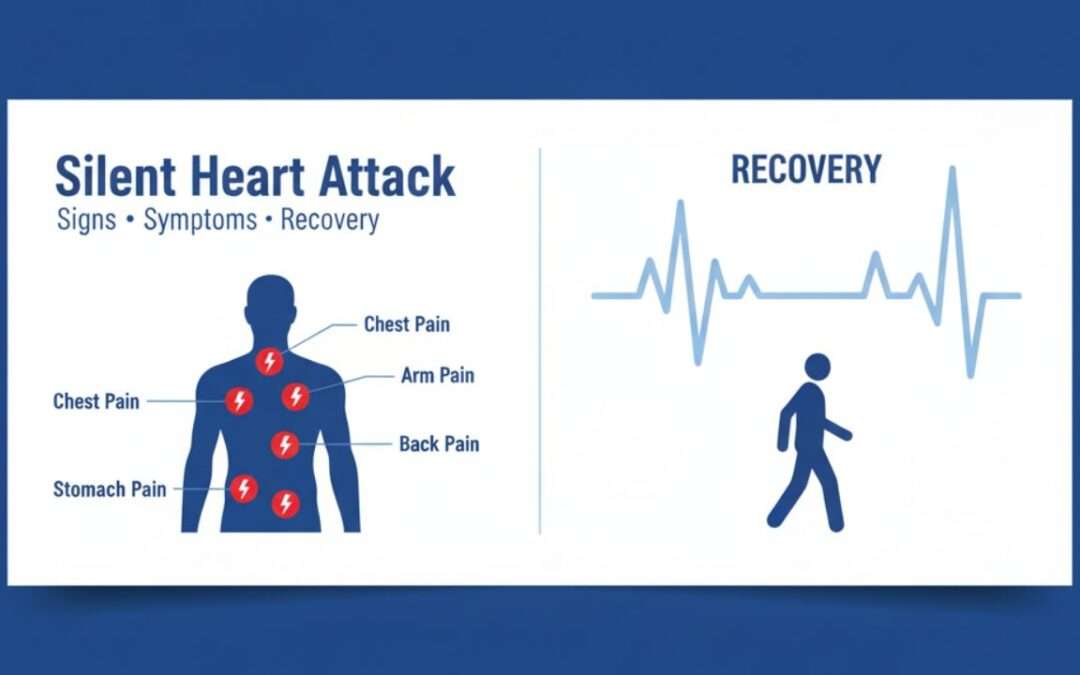
When we think of a heart attack, we usually imagine someone clutching their chest in severe pain. But did you know that some heart attacks happen silently, with little or no obvious symptoms? These are called silent heart attacks. They can be just as dangerous as regular heart attacks but often go unnoticed.
Since they don’t cause intense chest pain, people may not realize they have one until much later. This can lead to serious heart damage without any warning.
Silent heart attacks can affect anyone, but they are more common in people with diabetes, high blood pressure, or a history of heart disease. Understanding what a silent heart attack is, its symptoms, and what to do if you suspect you’ve had one is crucial for protecting your heart health.
What Is a Silent Heart Attack?
A silent heart attack happens when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, but the symptoms are so mild or unusual that they go unnoticed. Unlike typical heart attacks that cause severe chest pain, a silent heart attack may only cause minor discomfort, fatigue, or shortness of breath. Some people mistake it for indigestion or stress.
Since these attacks don’t feel like the dramatic heart attacks we see in movies, they often go undiagnosed until a doctor notices heart damage during a routine check-up. Even though the symptoms are mild, the damage to the heart can be severe.
Over time, it can lead to complications like heart failure or another heart attack. That’s why it’s important to know the subtle signs and risk factors of silent heart attacks.
How Common Are Silent Heart Attacks?
Silent heart attacks are more common than many people think. Studies show that nearly 50% of all heart attacks are silent. That means half of the people who have a heart attack may not even realize it.
They are especially common in older adults, people with diabetes, and women. Because the symptoms are subtle, silent heart attacks are often discovered only when doctors perform tests like an electrocardiogram (ECG) or MRI scan for another reason.
Women are more likely to experience silent heart attacks than men. Instead of the typical chest pain, women may feel tired, nauseous, or experience mild discomfort in the back or jaw. Since these symptoms are easy to overlook, many women delay seeking medical help, increasing their risk of complications.
The fact that silent heart attacks are so common makes it even more important to recognize their warning signs and take action early. As we understand the occurrence of a silent heart attack, it is also essential to know what the 4 silent signs of a heart attack are.
What Are the Symptoms of a Silent Heart Attack?
Unlike a regular heart attack, a silent heart attack doesn’t cause obvious, crushing chest pain. Instead, the symptoms can be mild and mistaken for other common issues like heartburn, anxiety, or even muscle pain. Here are some silent heart attack symptoms to watch out for:
Mild Chest Discomfort
You might have noticed severe chest pain from a regular heart attack. However, this heart attack may cause only mild symptoms. You will notice pressure, squeezing, tightness, or a dull ache in the chest. In some cases, people describe it as a sense of fullness or heaviness in the chest. It can last for a few minutes or come and go.
Shortness of Breath
Your routine activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or even resting, may cause a sign of a heart attack. Your heart struggles to pump oxygenated blood efficiently. Besides, you may experience shortness of breath without any chest discomfort. If you ever find yourself struggling with a simple task, it is time to consult a doctor.
Unexplained Fatigue
Even after a good night’s sleep, you feel tired, which can indicate a silent heart attack. When your heart is not functioning properly, the body receives less oxygen-rich blood, which leads to extreme fatigue. This kind of exhaustion may build up gradually or come on suddenly. Many people attribute it to stress, aging, or lack of sleep.
Pain in the Jaw, Neck, or Upper Back
You will notice pain spreading across the jaw, neck, shoulders, or upper back. This discomfort may be mild, come and go, or it may feel like a dull ache, tension, or pressure. You may assume it is due to your poor posture, stress, or muscle strain. However, if this pain is persistent or occurs alongside other symptoms such as shortness of breath or dizziness, it is best to seek medical evaluation.
Unexplained Sweating
When you notice a cold sweat without physical exertion, it is an important sign of a heart attack. In some cases, certain people experience sudden sweating, which is different from regular perspiration due to heat. When there is stress on your heart, you may feel clammy and cold.
Since the signs of a silent heart attack often go unnoticed, it is important to understand the signs and identify potential warning signs early.
What are the Risk Factors of Silent Heart Attack?
Certain factors increase the risk of having a silent heart attack. Some of the most common ones include:
High blood pressure
It forces the heart to work harder to pump blood throughout the body, and it can damage arteries, making them stiff and narrow. Hypertension often has no obvious symptoms; you may not realize this until complications arise.
Diabetes
If you have diabetes, then you might have a higher chance of nerve damage. It can make it harder to feel pain, meaning heart attack symptoms may go unnoticed. In addition, it contributes to the buildup of plaque in arteries, which can restrict blood flow to the heart.
Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels, reduces oxygen levels in the blood, and increases the risk of blood clots. It accelerates the buildup of plaque in the arteries, making them more likely to become blocked.
Obesity
Excess weight puts additional stress on the heart, and it is linked to other risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Losing just 5-10% of body weight can lead to significant improvements in heart health.
How Long Does It Take to Recover?
Recovery from a silent heart attack recovery time depends on how much damage has been done to the heart. If diagnosed early, lifestyle changes and medication can help prevent further problems. Most people can return to normal activities within a few weeks, but long-term care is necessary. Cardiac rehabilitation, diet changes, and regular exercise can help the heart heal.
The silent heart attack age is common in middle-aged and older adults. It is due to modern lifestyle factors such as stress, poor diet, and lack of exercise. However, youngsters also witness heart attack symptoms due to high stress or extreme workouts. It is important to seek medical help if you notice any symptoms. Besides, the recovery time may be different from patient to patient.
Conclusion
Silent heart attacks are dangerous as they often go unnoticed, yet they can cause significant heart damage over time. It is important to recognize the symptoms and risk factors. If you notice any symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. You can also book an appointment at Cardiology and Vascular Care Center, the leading cardiology clinic in Port Charlotte, to understand your symptoms.
FAQs
What Signs of Silent Heart Attack The Patients Must Know?
Symptoms may include mild chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, indigestion, or pain in the back, arms, or jaw. Some people mistake these signs for anxiety, flu, or acid reflux.
Who is Most Likely to Have a Silent Heart Attack?
The patients have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, smoking, lack of exercise, stress, and a family history of heart disease.
How Is a Silent Heart Attack Diagnosed?
A silent heart attack is often diagnosed during routine check-ups or when an ECG (electrocardiogram), echocardiogram, or blood test shows evidence of past heart damage.
What Are the Four Lethal Signs of a Silent Heart Attack?
- Unexplained fatigue or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Discomfort or pain in the chest, back, or jaw
- Cold sweats or dizziness
Yes, if left untreated, it can cause heart failure, irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), or increase the risk of a second, more severe heart attack.
What Lifestyle Changes Help Prevent a Silent Heart Attack?
Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, and getting regular check-ups can help reduce the risk.